Audacity Download
Our latest release
Audacity now offers a master channel feature and introduces exciting new real-time audio effects, giving you greater control and creativity while editing. These enhancements make it even easier to fine-tune your recordings and create polished soundtracks in real-time.
ACE Studio showcase
Bring your lyrics to life with ACE Studio, an AI-powered tool that generates realistic singing voices. Whether you’re composing a new track or just experimenting with melodies, ACE Studio lets you turn text into music effortlessly.
Record anything
Perfect for Podcasts, Voiceovers, or Simple Memos
Collaborate and Share with Audacity
Audio.com is the perfect online companion to Audacity. It enables seamless collaboration, easy version control, and quick sharing and publishing of your projects. Stay organized and share your work effortlessly with colleagues or clients.
All you need to create

Cross-platform
Audacity is fully compatible with Windows, macOS, and Linux, making it a versatile choice for anyone regardless of their operating system. No matter your platform, you can count on Audacity to provide consistent, high-quality performance.
Import, export, convert
Audacity supports all major audio formats, including the ability to import, export, and convert files between WAV, MP3, FLAC, Ogg, and more. Whether you’re working with audio for video or music production, Audacity makes file conversion simple and fast.
Plugin support
With support for a wide range of third-party plugins such as VST3 and Nyquist, Audacity allows you to expand its capabilities and elevate your audio production. Customize your workflow and add professional effects to your recordings with ease.

Deep audio analysis
Gain deeper insights into your audio with Audacity’s Spectrogram view, which visualizes frequencies. Additionally, the Vamp analyzers provide scientific analysis tools, helping you explore and understand your sound at a deeper level.
Popular in the FAQ
What Makes Audacity Stand Out?
Audacity is an immensely popular, free audio software that enables you to record, edit, and manipulate sound with ease. Whether you’re a hobbyist exploring music production or a content creator recording a podcast, Audacity provides the perfect platform for creative audio projects.
Who Can Benefit from Audacity?
Audacity is for anyone interested in audio experimentation or needing fast, effective audio editing. It’s the go-to tool for anyone working with sound, whether you’re editing recordings for work, creating content for social media, or just having fun with sound design.
Does Audacity Cost Anything?
Nope! Audacity has always been completely free to download and use, with no hidden costs. The developers have committed to keeping the software accessible to everyone.
How Open is Audacity’s Development?
Audacity is an open-source project, which means its code is freely available for anyone to explore, modify, or improve. A vibrant community of global contributors has played a huge role in shaping Audacity into the trusted tool it is today, and thanks to its open structure, there are a wide variety of third-party plugins to enhance its functionality.
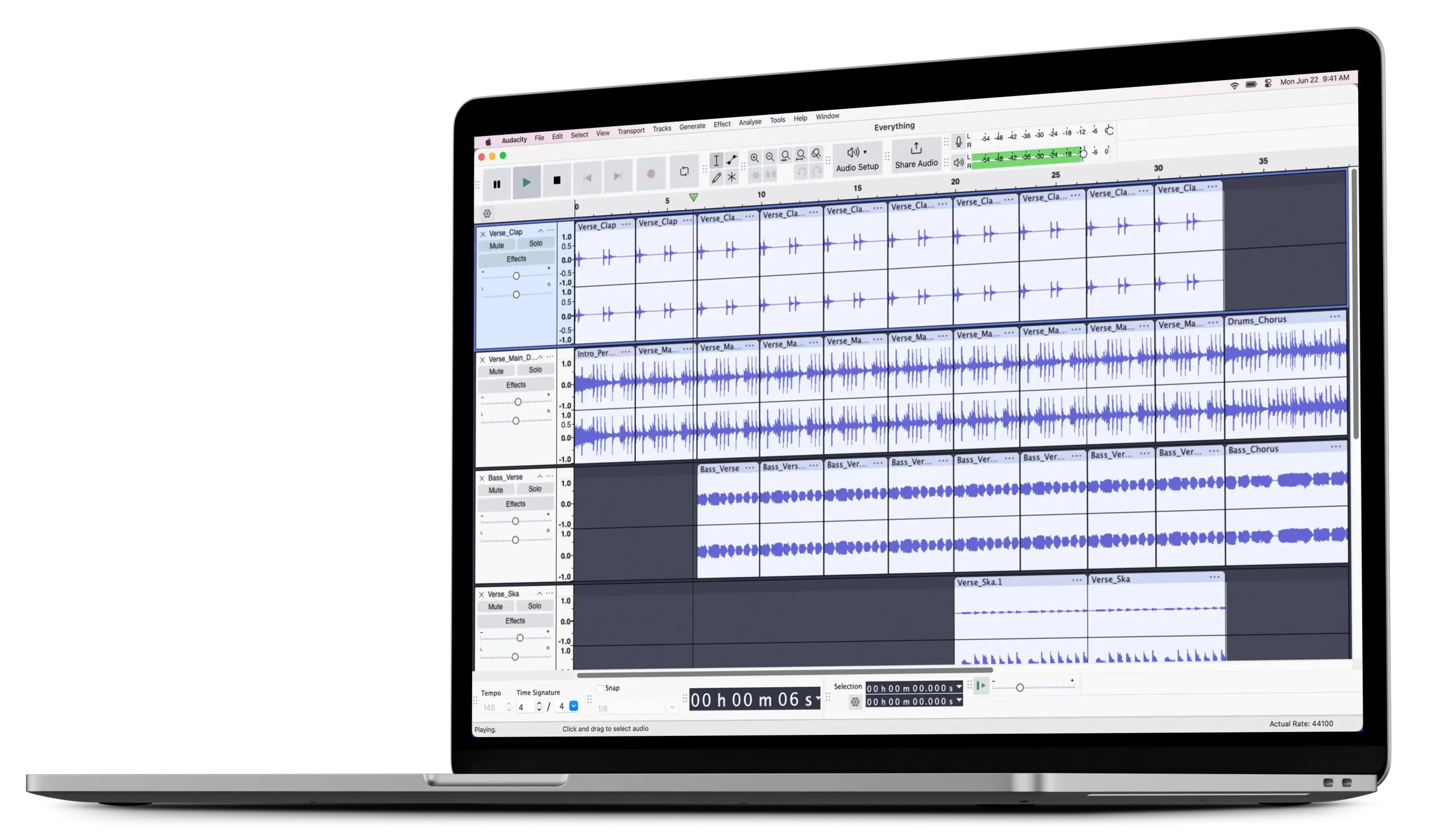
How to Use Audacity to Record & Edit Audio: A Beginner's Guide
Getting Started with Audacity
To download Audacity, visit v2-audacity.com, where you’ll be directed to the correct download page for your operating system. After downloading the installer, run it and follow the installation prompts. Once installed, open the program to start a new project. When you first launch Audacity, you’ll see a blank project interface. This includes various menus and buttons for controlling your recording and editing. Before diving into your recording, it’s important to configure a few settings for your project.
Configuring Project Settings
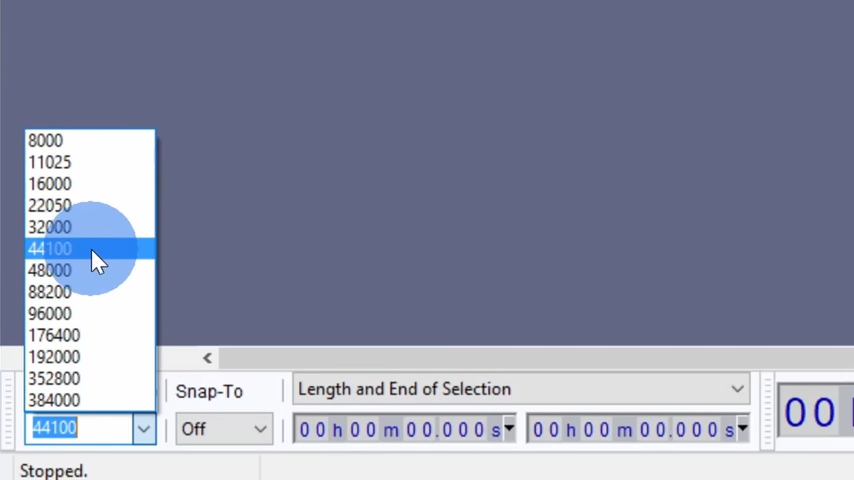
In the bottom left corner of the screen, you’ll notice a setting called the “Project Rate,” which is also known as the sample rate. The sample rate determines how often the audio is sampled during recording. Higher sample rates offer greater accuracy, but they also result in larger file sizes.
For most standard audio projects, a sample rate of 44,100 Hz is sufficient. However, for today’s tutorial, I will use 48,000 Hz, which is commonly used for video production and ensures high-quality sound.
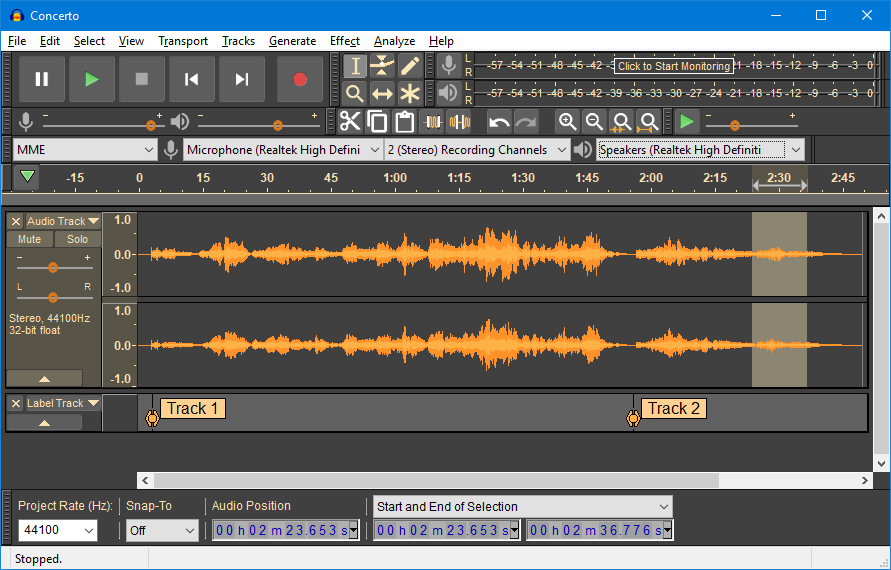
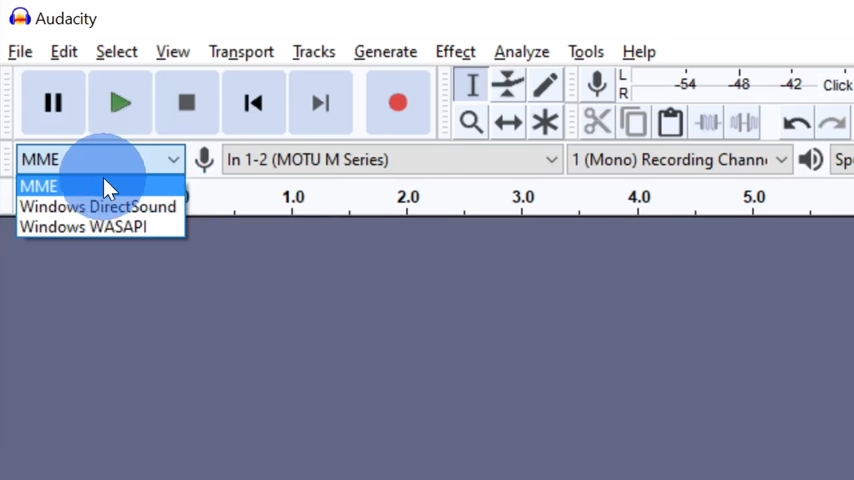
Selecting Audio Drivers and Input Devices
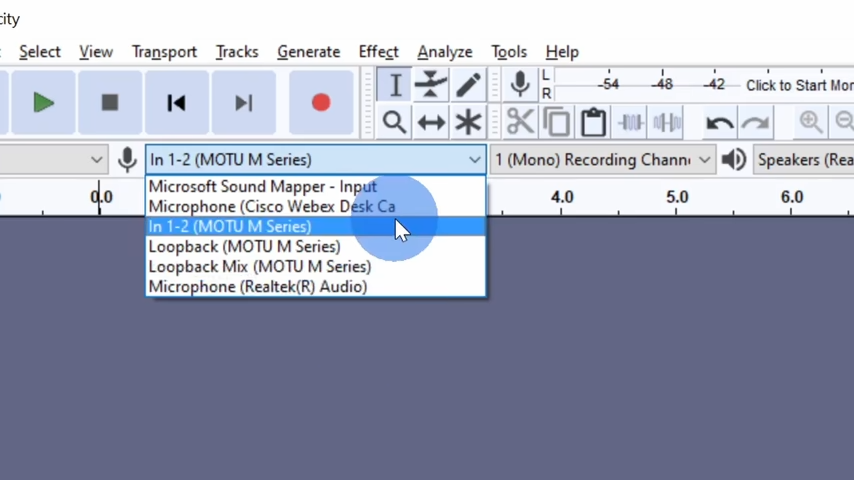
At the top of the screen, you’ll find a dropdown menu for audio drivers. There are several options to choose from: MME: The oldest option, with the greatest compatibility. Windows DirectSound: More modern, but can have higher latency. Windows WASAPI: The newest and most efficient option for low-latency recording. I’ll be using the default MME option in this tutorial. Right next to the driver dropdown, you can select which microphone to use for recording. If you have multiple microphones connected to your computer, such as a built-in laptop mic or an external USB mic, you can easily switch between them. To record in stereo or mono, you can select the corresponding option. Most microphones are mono, so unless you’re recording from a stereo setup, you’ll likely leave this on mono. Lastly, don’t forget to select your playback device. If you’re using speakers or headphones connected to your computer, select them here to listen to your recordings.
Setting Recording Levels
Now that your microphone is selected, it’s time to adjust your recording levels. In the top bar, there is a recording meter that shows your current audio input levels. It’s crucial to monitor these levels to ensure you’re not recording too quietly or too loudly.
If your recording level spikes too high (hitting the red zone), it may cause audio clipping, where parts of the sound are distorted. Try to keep the levels in the green range to avoid this. If necessary, you can adjust your microphone gain or use the input volume slider in Audacity to get the right balance.
Tip: It’s a good practice to do a test recording before starting your full project to ensure everything sounds good.
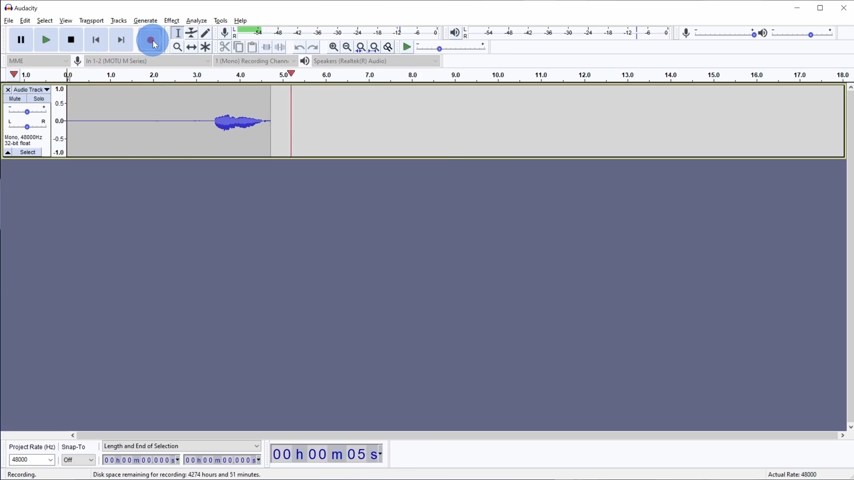
Recording Your Audio
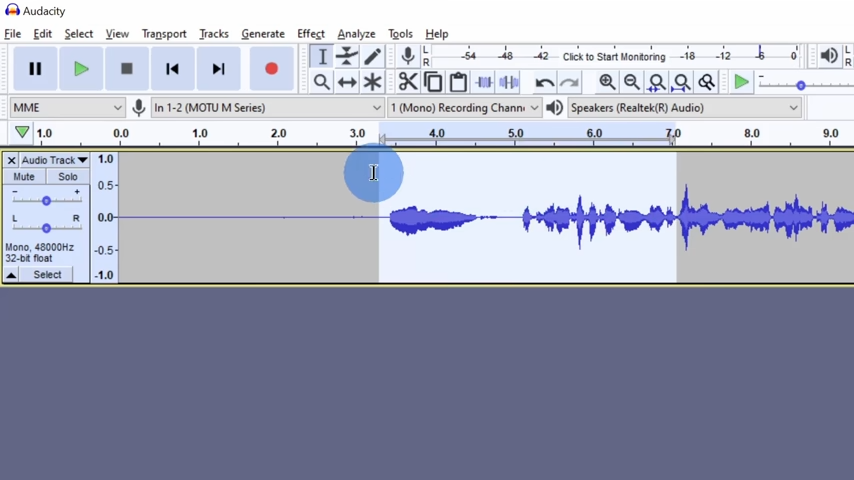
Once everything is set up, you’re ready to start recording. Press the red Record button to start capturing audio. As you speak, you’ll see the waveform representing your voice on the screen. The horizontal axis shows time, while the vertical axis represents the loudness of your voice.
Pro Tip: When starting a recording, wait a second before speaking. This creates a natural buffer at the beginning of your audio, which is useful if you need to edit out any unwanted noise later
Reviewing Your Recording
After recording, you’ll see the waveform of your audio. You can use the Play button (or press the spacebar) to listen to your recording. If necessary, you can adjust the playback volume using the device settings you selected earlier.
You can also zoom in on your waveform to see more detailed information about the audio. This is useful for editing, as it allows you to pinpoint specific sections you may want to modify.
Audacity
Audacity is an easy-to-use, multi-track
audio editor and recorder for Windows, macOS, GNU/Linux and other operating systems.
Audacity is free, open source software.
@Audacity 2025


